
Future-Ready Rural Health: The RHT Operating Model for Sustainable Growth
Executive Operating Summary
CMS's $50 billion Rural Health Transformation (RHT) Program is a historic opportunity to modernize rural care delivery, stabilize providers, and strengthen local economies. But funding alone does not create impact. Lasting transformation requires disciplined execution: clear ownership, aligned incentives, and an operating model that converts strategy into results.
The Garage's RHT Operating Model is a living operating system for rural health transformation, with embedded data, automation, governance, and continuous learning loops. It aligns people, processes, governance, and technology into a single, ROI-anchored framework that rural networks can operate day-to-day, rather than just plan against.
This model is designed to:
- Realize operational and financial ROI within six months, primarily through reduced administrative burden, improved revenue capture, and early utilization gains.
- Deliver measurable clinical outcome improvements within 12-24 months, aligned to roadmap targets such as improved chronic disease control, reduced avoidable emergency department use, and increased preventive and wellness visit completion.
- Prepare rural systems for multi-payer value-based care by unifying data, automating measurement, and embedding intelligence directly into clinical and operational workflows.
- Advance health equity, behavioral health integration, and community impact by connecting clinical care with community-based organizations (CBOs), SDOH insights, and local economic priorities.
- Reinforce rural hospitals and clinics as anchor institutions that sustain local employment, infrastructure, and economic resilience.
This operating model explicitly aligns with key RHT strategic aims: making rural America healthier (Pieces 1, 3, 4, 10), sustaining access (Pieces 4, 6, 7, 9), strengthening the workforce (Pieces 5, 8, 10), enabling innovative care and payment (Pieces 2, 3, 6, 7), and advancing technology and security (Pieces 2, 3, 8, 9).
The goal is simple: make rural health transformation operable, with clear accountability, execution cadence, and measurable return on investment.
Scope and Focus of the RHT Operating Model
The Garage's RHT Operating Model is designed to focus execution energy on areas that deliver the fastest, most sustainable impact for rural health systems. At its core, the model brings together the essential capabilities needed to modernize care delivery while remaining adaptable to evolving technology, payment, and policy environments.
It begins with a care delivery transformation - integrating clinical, behavioral health, and community-based care into a cohesive operating approach. This is supported by unified data and interoperability, connecting clinical, claims, financial, and social determinants of health (SDOH) sources to enable longitudinal insights and coordinated action.
To reduce administrative burden and improve efficiency, the model embeds intelligence and automation directly into daily workflows, surfacing prioritized actions for care teams. Strong governance and operating cadence ensure clear ownership, decision rights, and performance review rhythms that translate strategy into sustained execution.
Every initiative is anchored in ROI-driven performance management, tying efforts to measurable clinical, operational, workforce, and financial outcomes over defined time horizons. The model also emphasizes network coordination and partnership enablement, fostering collaboration among hospitals, clinics, behavioral health providers, community-based organizations, and payers to scale impact regionally.
Finally, workforce sustainability and resilience remain central, equipping teams with the tools, visibility, and support needed to work at the top of their licenses and thrive long-term.
By focusing on these capabilities, the RHT Operating Model accelerates readiness, reduces fragmentation, and empowers rural organizations to deliver modern, integrated care that meets their communities' needs.
Start with Readiness
Transformation begins with a structured readiness assessment that establishes baselines and ROI-anchored performance objectives across six domains:
- Data Interoperability: EHR-agnostic, FHIR- and TEFCA-ready connectivity; USCDI-aligned data; multi-source integration across clinical, claims, labs, prescriptions, and SDOH.
- Workforce Capacity: Staffing sufficiency, burnout risk, role clarity, and ability to work at the top of license.
- Equity and Access: SDOH-driven insight into transportation, housing, food insecurity, broadband gaps, and geographic barriers.
- Financial and Multi-payer Readiness: Denial patterns, revenue leakage, payer mix, and readiness for Medicaid, Medicare, and commercial value-based contracts.
- Digital-First Readiness: Telehealth, remote monitoring, asynchronous care, and digital engagement capabilities.
- Behavioral Health Integration: Capacity to support mental health, substance use disorders, and behavioral comorbidities alongside chronic disease management.
The outputs are:
- A quantified baseline across clinical, operational, financial, and equity dimensions
- A set of ROI-anchored performance objectives tied to defined timeframes and roadmap milestones
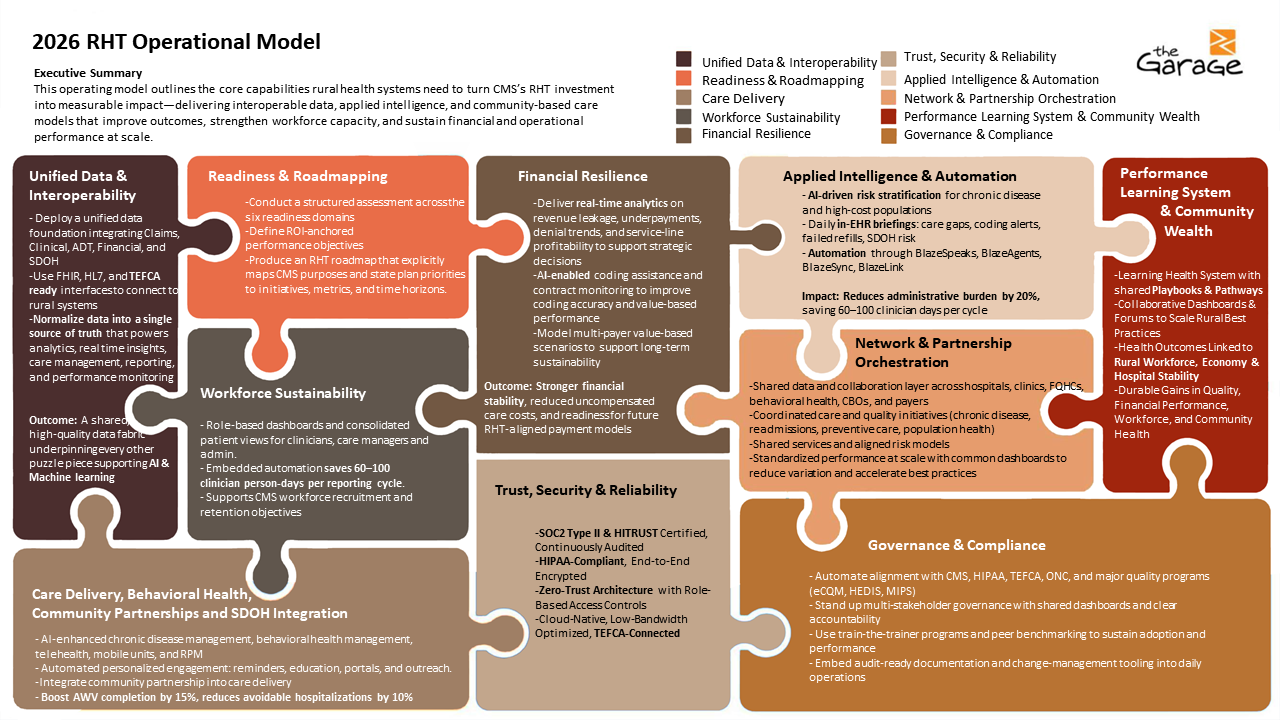
The Ten Puzzle Pieces of the RHT Operating Model
Think of the model as a ten-piece puzzle: each piece delivers value independently, but full impact is achieved when they interlock under shared governance, metrics, and learning.
Readiness and Roadmapping
- Conduct a structured assessment across the six readiness domains, including baseline metrics for chronic disease, utilization, equity, workforce, and financial performance.
- Define ROI-anchored performance objectives, such as:
- 15% reduction in uncontrolled diabetes within 12 months.
- 15% increase in preventive screening completion in 12 months.
- 10% reduction in avoidable ED visits within 12 months.
- Produce an RHT roadmap that explicitly maps CMS purposes and state plan priorities to initiatives, metrics, and time horizons.
Unified Data and Interoperability
- Deploy a unified data foundation integrating EHR, claims, ADT, labs, prescriptions, financial, and SDOH data into a longitudinal patient record.
- Use FHIR-, HL7-, and TEFCA-ready interfaces to connect rural systems without requiring EHR replacement.
- Normalize data into a single source of truth that powers analytics, real-time insights, care management, reporting, and performance monitoring.
- Outcome: A shared, high-quality data fabric underpinning every other puzzle piece supporting AI and machine learning capabilities.
Applied Intelligence and Automation
- Use AI-driven risk stratification to identify patients at the highest risk for disease progression, readmission, or avoidable ED use.
- Surface daily in-workflow briefings: open care gaps, suspected codes, recent discharges, failed refills, elevated SDOH risk, and behavioral-health flags.
- Automate outreach, coding prompts, quality reporting, and care management workflows using embedded automation tools to reduce manual work.
- Impact: Approximately 20% reduction in administrative burden, saving 60-100 clinician person-days per reporting cycle and enabling earlier, targeted interventions.
Care Delivery, Behavioral Health, Community Partnerships, and SDOH Integration
- Embed AI-enhanced chronic disease and behavioral health management into primary care, including telehealth, mobile units, and remote monitoring capabilities.
- Integrate community partnerships directly into care delivery: transportation, food access, housing support, broadband/connectivity programs, and local social services.
- Drive automated, personalized patient engagement: AWV reminders, screening outreach, chronic care check-ins, and education, tuned to SDOH risk profiles.
- Targets (illustrative percentages based on representative networks):
- 12-15% increase in AWV completion in 18 months.
- 15% reduction in uncontrolled diabetes in 12 months.
- 10% reduction in avoidable ED visits in 12 months.
- Governance: Care Transformation Council with CBO representation, ensuring clinical and community interventions are coordinated.
Workforce Sustainability
- Role-based dashboards and consolidated patient views for clinicians, care managers, and administrative staff so they work from a single, prioritized queue.
- Automate reporting, task generation, and care coordination to reduce manual work, supporting recruitment and retention by lowering burnout.
- Offer ongoing training and coaching (train-the-trainer) to build digital and analytical skills within rural teams.
- Outcomes: 20% reduction in administrative burden for care managers, improved staff satisfaction, and lower turnover over 12-24 months.
Financial Resilience
- Deliver real-time analytics on revenue leakage, underpayments, denial trends, and service-line profitability to support strategic decisions.
- Use AI-enabled coding assistance and contract monitoring to improve coding accuracy and value-based performance, targeting a 5-8% improvement in revenue capture in year one.
- Model multi-payer value-based scenarios (Medicare, Medicaid, commercial) to right-size risk, optimize payer mix, and support long-term sustainability.
- Outcome: Stronger financial stability, reduced uncompensated care costs, and readiness for future RHT-aligned payment models, expressed as percentage improvements rather than dollar amounts.
Network and Partnership Orchestration
- Stand up a shared analytics and collaboration infrastructure for regional partners: hospitals, clinics, FQHCs, behavioral health providers, CBOs, and payers.
- Enable coordinated quality initiatives (for example, chronic disease, readmissions, preventive care), shared service models (telehealth, specialty consults, revenue cycle management), and risk-sharing arrangements.
- Use standardized dashboards and scorecards to reduce variation, track joint performance, and drive best-practice dissemination.
- Goals (illustrative percentages):
- Integrated data sharing and communication workflows across 100% of participating partners within 12 months.
- 15% increase in shared service utilization within 24 months and a meaningful increase in collaborative quality improvement projects across the network.
Governance, Compliance, and Operating Cadence
- Establish a multi-stakeholder Governance Council responsible for strategy, policy, and oversight; designate data stewards and program leads with explicit accountabilities.
- Automate compliance and reporting for CMS, HIPAA, TEFCA, eCQM, HEDIS, and MIPS using the unified data layer and embedded reporting tools.
- Define a clear cadence:
- Monthly operational reviews using dashboards and key indicators.
- Quarterly roadmap and performance refresh based on outcomes and ROI.
- Annual strategic review to align with evolving CMS programs and state priorities.
Trust, Security, and Reliability
- Operate on SOC 2 Type II- and HITRUST-aligned, HIPAA-compliant infrastructure with end-to-end encryption, role-based access, and robust disaster recovery.
- Implement zero-trust architecture and continuous security monitoring, accommodating rural connectivity constraints with a cloud-native, low-bandwidth-optimized design.
- Maintain continuous regulatory alignment and measure updates to keep the platform value-based-care-ready as standards evolve.
Performance Learning System and Community Wealth
- Build a learning health system where data from each facility and network is fed back into shared playbooks, pathways, and templates.
- Use collaborative forums and dashboards to review what works, codify interventions, and spread successful models across rural partners.
- Explicitly link health outcomes to community wealth: local hiring, training pipelines, local vendor spend, broadband and housing investments, and stability of rural hospitals as anchor institutions.
- Outcome: Durable, compounding gains in quality, financial performance, workforce resilience, and local economic health, expressed through percentage improvements in key indicators.
From Vision to Value: Phased Timeline
The operating journey aligns with the RHT workplan timelines while making ROI expectations explicit.
- Months 1-3 (Phase 1 - Assess and Configure):
- Readiness assessment, baseline establishment, data integration planning, workflow configuration.
- Months 4-6 (Phase 2 - Go-Live and Initial ROI):
- Go-live in first wave of facilities with AI briefings, dashboards, and core automations; early operational and financial ROI demonstrated through percentage reductions in administrative burden, denial rates, and coding gaps.
- Months 6-18 (Phase 3 - Network Scale and Multi-payer Readiness):
- Expansion to additional facilities and partners, shared services, and collaborative quality initiatives; measurable percentage improvements in chronic disease control, preventive screening, AWV completion, and avoidable ED visits.
- Months 18-24+ (Phase 4 - Institutionalize and Optimize):
- Full performance learning system in place, annual strategy refresh cycles, and ongoing optimization to meet and exceed ROI-anchored objectives across clinical, financial, workforce, and community metrics.
Measuring What Matters
This table harmonizes the metrics from the workplan and operating narrative into a single view of what success looks like, using percentages rather than dollar amounts and positioning them as illustrative outcome ranges based on representative networks.
| Dimension | Leading Indicators (0-6 months) | Lagging Outcomes (12-24 months) |
|---|---|---|
| Access and Engagement | AWV outreach rates, telehealth and mobile-unit utilization, patient response rate (for example, 30% improvement with AI outreach) | 12-15% increase in AWV completion; 15% increase in preventive screening rates |
| Behavioral and Chronic Health | Behavioral health screening rates, risk-stratified registries, intervention, and adherence | 15% reduction in uncontrolled diabetes; 8-12% reduction in readmissions for chronic conditions |
| Workforce Resilience | Task automation adoption, training completion, and satisfaction survey scores | 60-100 person-days saved per reporting cycle; reduced burnout and lower turnover (expressed as percentage decreases) |
| Financial and Contracting | Denial rates, coding accuracy, payer-mix performance | 5-8% improvement in revenue capture; noticeable percentage reductions in avoidable hospitalizations and ED visits contributing to overall cost efficiency |
| Digital Maturity | Time to insight (dashboard latency), remote-monitoring enrollment, and telehealth uptime | Faster decision cycles and sustained digital-first care models across rural sites, visible as percentage gains in digital utilization and reliability |
| Community and Equity | Number of active CBO partnerships, SDOH-driven referrals, and high-risk SDOH engagement | Reduced disparities in access and outcomes, percentage increases in patients successfully connected to community resources and supports |
| Governance and Learning | Cadence adherence (monthly and quarterly reviews), number of shared playbooks, and network initiatives | Institutionalized continuous improvement and network-wide performance gains, measured as consistent percentage improvement across agreed KPIs |
From Strategy to Sustained Performance
Operating RHT at Scale
Rural transformation is no longer about pilots or isolated projects. It is about operating a unified model that delivers consistent, measurable value for patients, providers, and communities.
The Garage's RHT Operating Model provides rural networks and states with a disciplined, repeatable way to convert the RHT opportunity into durable clinical, financial, workforce, and community outcomes-measured through clear, percentage-based performance improvements over time.
The next step is execution.
Establish your readiness baseline, align your roadmap to CMS priorities, and activate the data, intelligence, and governance needed to make rural health transformation real-and sustainable.
Ready to learn more? Request more information today !
- I'm curious. I'd like
to set up a demo - What does the
platform do? - Tell me more about
the Garage - What has been the
platform's impact?
